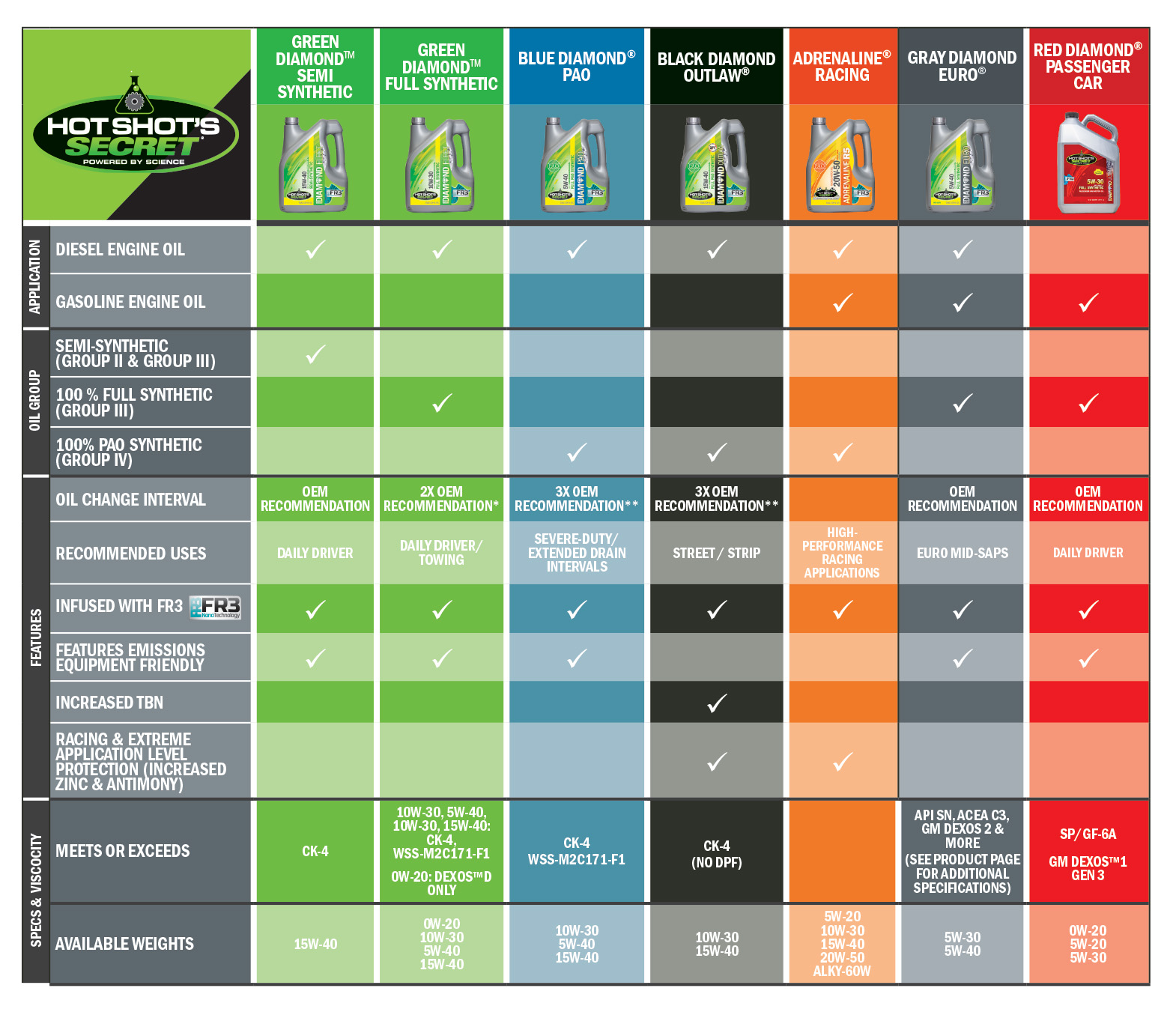
When it comes to ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of your diesel RV, selecting the right engine oil type is crucial. Diesel engines are specially designed to handle high torque and heavy-duty workloads, which means the demands they place on engine oil are distinct from those of gasoline engines.
According to industry data, approximately 400,000 RVs with diesel engines are on the road today, each requiring specialized care and maintenance to avoid costly repairs.
With various oil formulations available, understanding the differences between them becomes key for every RV owner. This comprehensive guide will take you through the essential aspects of diesel engine oil, covering types, viscosity ratings, API classifications, and best maintenance practices.
By the end of this article, you will have the knowledge to choose the proper engine oil, maintain your RV efficiently, and ensure that your adventures on the road remain safe and enjoyable.
Table of Contents
- 1. Understanding Diesel Engine Oil Types
- 2. The Importance of Oil Viscosity in Diesel Engines
- 3. API Classifications for Diesel Engine Oils
- 4. Best Maintenance Practices for Diesel RVs
- 5. The Role of Oil Sampling and Analysis
1. Understanding Diesel Engine Oil Types
When it comes to diesel engine oils, the options can be broadly categorized into two types: conventional and synthetic. Conventional oils, derived from crude oil, have been the standard choice for many years due to their effective lubricating properties.
However, they are prone to faster degradation, necessitating more frequent oil changes.
In contrast, synthetic oils, although often more expensive, specialize in providing superior performance in extreme temperatures and heavy-duty applications. They enhance lubrication and can significantly extend service intervals, making them a popular choice among manufacturers and mechanics.
Conventional Vs. Synthetic Oils
Conventional oil is made from refined crude oil and typically requires you to change it every 3,000 to 5,000 miles. This is especially true in high-stress conditions often encountered by diesel engines.
On the other hand, synthetic oils can last 10,000 to 15,000 miles without degradation.
Given that most diesel RVs might travel significant distances, the higher cost of synthetic oils often pays off in terms of long-term engine health.
The Role of Additives in Diesel Oils
Additives are crucial in both conventional and synthetic oils because they enhance the oil’s performance characteristics. Common additives include detergents, dispersants, and anti-wear agents.
They help in maintaining engine cleanliness by preventing sludge buildup, improving overall performance, and extending oil life.
For diesel engines, additives that reduce soot and oxidation are particularly important to mitigate the effects of combustion byproducts.
Understanding Viscosity Ratings
Viscosity is a measure of an oil’s resistance to flow, which is particularly critical in diesel engines. For instance, an oil rated 15W-40 performs well at high temperatures while providing adequate protection during colder conditions, designated by the ‘W’ (winter) rating.
Diesel engines generally perform best with oils in the 15W-40 or 10W-30 range, depending on environmental conditions and specific engine requirements.
This table shows the comparative aspects of different diesel engine oils, illustrating that synthetic oils generally offer higher performance specs than conventional oils, which is crucial for the demanding operations of diesel engines. While conventional oil is sufficient for regular driving conditions, synthetic oils provide an edge in durability and performance in challenging environments, thereby reducing maintenance frequency.
- Diesel engine oils fall into conventional and synthetic categories, each with unique benefits.
- Regular oil changes are essential for conventional oils; synthetic oils allow for longer intervals.
- Additives in oils enhance performance and prolong engine life.
2. The Importance of Oil Viscosity in Diesel Engines
The viscosity of oil plays a critical role in the lubrication process of diesel engines, impacting how well the engine operates under different temperature conditions. Viscosity is essential not only for flow but also for maintaining adequate pressure within the engine.
Cold Weather vs. Hot Weather Viscosity
In cold temperatures, thicker oils can be sluggish, leading to a lag in lubrication when starting the engine. Oils like 10W-30 perform better in cold climates as they remain less viscous.
Conversely, in hotter conditions, oils rated 15W-40 can provide the necessary thickness to protect engine parts from overheating while maintaining adequate flow.
Impact of High Viscosity on Engine Components
Higher viscosity oils can create more resistance during cold starts. This could lead to increased wear as the oil takes longer to reach critical engine components.
Additionally, using oils with improper viscosities can lead to lower fuel efficiency and engine strain, potentially resulting in premature wear or failure.
Recommendations for Seasonal Changes
It is often wise to reassess your oil choice based on seasonal temperature changes. In climates that vary significantly, switching between 10W-30 in colder months and 15W-40 during hotter months can optimize engine performance and longevity.
Always consult your owner’s manual for specific recommendations related to your RV model.
- Viscosity is crucial for engine performance, affecting flow and lubrication efficiency.
- Oil choice should be temperature-specific, changing with seasons for optimal protection.
- Using incorrect viscosity can lead to increased wear and reduced engine efficiency.
3. API Classifications for Diesel Engine Oils
The American Petroleum Institute (API) sets rigorous standards for engine oils, enabling consumers to select products that meet specific performance criteria. API classifications such as CJ-4 and CK-4 denote oils that fulfill the high demands of diesel engines.
Deciphering API Ratings
API designations typically consist of a letter denoting the oil category followed by a number indicating the revision level. For diesel engines, oils rated CJ-4 or CK-4 are designed to provide better protection against soot and heat compared to older standards.
Understanding these ratings helps you select oils that align with your RV’s operational demands.
Comparison of CJ-4 and CK-4 Standards
The transition from CJ-4 to CK-4 reflects advancements in engine design, particularly regarding emission control and efficient combustion. CK-4 oils have improved thermal stability and protection against wear and deposits in the engine.
This makes them preferable for modern diesel engines that operate in harsher conditions.
Consequences of Using Non-API Certified Oils
Using oils that do not carry API certification can pose risks to engine performance and longevity. Non-certified oils may fail to provide adequate protection against wear, deposits, and thermal breakdown, which could lead to costly repairs or even engine failure.
This table provides a clear snapshot of the differences between API classifications crucial for diesel engines. Notably, CK-4 oils are ideal for new diesel engines due to their advanced formulation, while CJ-4 oils may still serve older vehicles well.
The emergence of FA-4 oils provides options for owners needing improved performance in specific applications, especially under heavy loads or in extreme temperatures.
- API classifications ensure oils meet performance benchmarks required for diesel engines.
- CK-4 oils are preferred for modern engines due to their improved stability and wear protection.
- Using oils lacking API certification can jeopardize engine health and performance.
4. Best Maintenance Practices for Diesel RVs
Keeping your diesel RV engine in top condition is paramount for ensuring long-term reliability and performance. Regular maintenance practices include timely oil changes, monitoring oil levels, and understanding the signs of oil degradation.
When to Change Oil and Filters
Most diesel RV engines require oil changes approximately every 10,000 to 20,000 miles, depending on usage. Frequent trips over rough terrain, heavy towing, or prolonged idling can strain your engine and oil, necessitating more frequent changes.
It’s advisable to consult your specific manufacturer’s recommendations for oil change intervals based on engine type and usage.
Signs of Oil Degradation
Visually inspecting oil quality should be part of your routine maintenance. Look for dark, gritty oil, or signs of foam that indicate contamination.
If the oil level consistently drops without apparent leaks, this could point to excessive consumption or underlying engine issues.
Use the dipstick to regularly check if the oil level needs topping up or changing.
Importance of Maintenance Logs
Maintaining detailed logs of your RV’s maintenance, including oil changes, is vital for tracking engine health. This documentation is especially crucial for warranty claims and resale value.
By documenting dates and mileage, you can also predict when the next service will be required, aiding in proactive management of your RV.
This maintenance schedule table provides practical guidelines on oil change intervals under various driving conditions often encountered by diesel RVs. Adapting the oil change frequency based on how you use your RV can significantly influence engine reliability and performance, preventing unpleasant surprises down the road.
- Oil changes should align with driving conditions and manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Visual checks for oil quality can help identify when oil needs changing.
- Keeping maintenance logs is essential for effective engine management and resale value.
5. The Role of Oil Sampling and Analysis
Conducting oil sampling can provide essential insights into the internal condition of your RV’s engine. This process not only aids in maintaining your engine but can also save you from unexpected mechanical failures.
How to Perform Oil Sampling
To collect an oil sample, use a syringe or a dedicated sampling kit to extract oil from the engine. Ideally, the sample should be taken during an oil change when the oil is warm, ensuring that it flows better and provides a more accurate representation of its condition.
Follow the specific instructions provided by your oil analysis service for the best results.
Interpreting Oil Analysis Reports
Once your oil is analyzed, the laboratory will provide a report detailing wear metals, contaminants, and overall oil health. Key metrics include the presence of metals like copper, lead, and iron, which indicate wear, while other elements may signal contamination, such as coolant or dirt from external sources.
Understanding these results allows you to make informed decisions about when to change oil or address engine concerns.
Revising Maintenance Based on Analysis
Regular oil analysis helps tailor your maintenance practices to the specific needs of your engine. For instance, if wear metals are elevated, it may indicate that the engine’s components are wearing prematurely.
This information can prompt you to investigate further, potentially mitigating costly repairs.
- Oil sampling identifies contaminants and wear materials in your engine oil.
- Understanding analysis reports helps inform maintenance decisions and practices.
- Regular analysis can extend oil change intervals and enhance engine longevity.
FAQ
1. What type of engine oil should I use for my diesel RV?
The type of engine oil you should use depends on your RV’s specifications. Generally, synthetic oils like 5W-40 or 15W-40 are recommended for their superior performance and longer change intervals, especially in demanding conditions.
Always consult your owner’s manual for specific recommendations for your engine.
2. How often should I change my RV diesel engine oil?
Most diesel engine manufacturers recommend oil changes approximately every 10,000 to 20,000 miles, depending on your driving conditions and engine type. If you frequently tow or drive in harsh conditions, it may be necessary to change the oil sooner.
Regular maintenance is essential for longevity.
3. Can I use conventional oil in my diesel RV?
Yes, conventional oil can be used, but it is less preferred due to its shorter life span and performance characteristics. A synthetic or semi-synthetic oil will provide better protection and efficiency, particularly for high-operating temperatures common in diesel engines.
4. Why is oil viscosity important?
Oil viscosity affects how well the oil flows through your engine. The viscosity rating indicates the oil’s thickness at different temperatures.
Using oil with the correct viscosity ensures better lubrication and protection, especially during cold starts or high-temperature conditions.
5. What are API classifications, and why are they important?
API classifications indicate the performance standards met by motor oils. For diesel engines, oils marked as CJ-4 or CK-4 provide enhanced protection and efficiency compared to lower-rated oils.
Selecting an oil with the appropriate API classification is critical for engine health.
Conclusion
Selecting the right engine oil type for your diesel RV is crucial for achieving maximum performance and longevity. By understanding the different oil types, viscosity, and maintenance practices, you can prevent expensive repairs and ensure that your engine runs smoothly.
Regular oil changes, coupled with oil analysis, contribute to the overall health of your engine, safeguarding your tomorrow’s adventures on the road.
Always remember, when in doubt, refer to your RV’s owner manual for the most accurate recommendations!