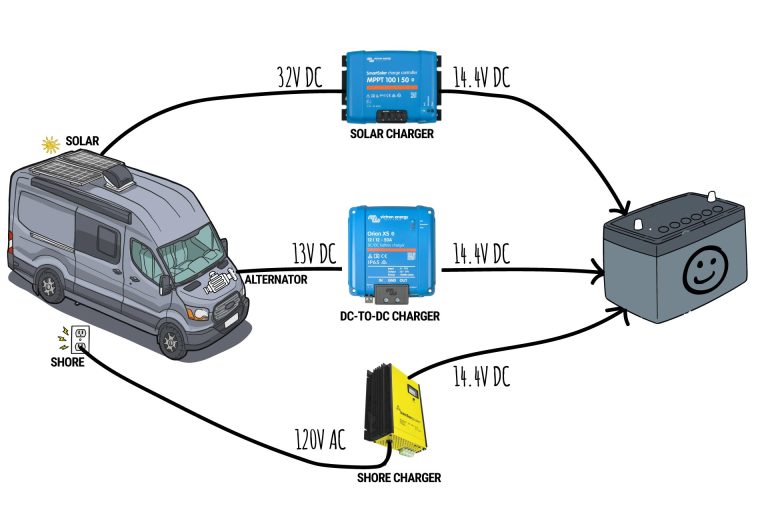
Being on the road in a campervan is a liberating experience, allowing adventurers to explore and enjoy diverse landscapes. However, this freedom comes with the complexity of managing an electrical system that often operates on both AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) power.
Understanding campervan electrical issues and their solutions is crucial for a safe, enjoyable journey.
Statistics indicate that electrical problems are among the most common issues reported by campers, leading to disruptions in the joy of exploration. This guide is designed to assist campervan owners by exploring common electrical problems, troubleshooting techniques, and maintenance tips to ensure a reliable electrical system.
We will address components like converters, inverters, batteries, and grounding—essential areas to master for anyone looking to enhance their campervan experience.
Whether you’re a beginner or have some experience, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to tackle campervan electrical issues effectively.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Campervan Electrical Systems
- Common Electrical Issues in Campervans
- Troubleshooting Electrical Components
- The Role of Converters and Inverters
- Grounding Issues in Campervans
- Maintaining Battery Health
- Importance of Regular Inspections
- Troubleshooting FAQs
Understanding Campervan Electrical Systems
A campervan electrical system primarily operates on both AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) power. Understanding the differences between these power types is essential for diagnosing and resolving issues efficiently.
DC power usually comes directly from the camper’s batteries and is used to fuel low-voltage appliances like lights and water pumps.
Conversely, AC power is linked to shore power or a generator, which powers high-demand appliances such as microwaves and air conditioners.
AC vs. DC Appliances
It’s crucial to know what type of electricity each appliance requires. Generally, DC appliances should be connected to the camper’s battery system, while AC appliances need to be plugged into a power source.
Table 1 shows typical power requirements:
Analysis of Table 1: This table highlights the distinctions between various campervan appliances and their current requirements. Understanding whether an appliance runs on AC or DC power ensures proper connections and prevents circuit overloading.
For example, connecting a high-wattage appliance like a microwave to a DC circuit may exceed the circuit’s capacity, resulting in blown fuses or worse.
Knowing the specific requirements assists campervan owners in making informed decisions about their electrical systems.
Common Electrical Components
Knowing the standard components in your campervan electrical setup can aid troubleshooting. These typically include:
- Batteries: Store energy for DC appliances.
- Converters: Convert AC power to DC.
- Inverters: Allow DC power to run AC appliances.
- Fuses/Breakers: Protect electrical circuits.
Power Conversion Basics
Power conversion is integral to campervan electrical systems, ensuring the appropriate current flows to appliances. Understanding how converters and inverters operate helps owners identify issues that arise from incorrect connections or component failures.
Key Takeaway:
- AC power is used for high-demand appliances, while DC powers basic functions like lighting.
- Familiarity with appliance power requirements can prevent issues related to incorrect connections.
- Understanding your electrical components will aid in effective troubleshooting.
Common Electrical Issues in Campervans
Many campervan owners encounter a variety of electrical problems that can lead to inconvenience during their adventures. Effective diagnostics often hinge on recognizing patterns in symptoms and behaviors of electrical components.
Identifying Electrical Symptoms
Common symptoms include:
- Dimming or flickering lights: May indicate weak connections or an insufficient power supply.
- No power to outlets: Often due to tripped breakers or blown fuses.
- Inconsistent power to appliances: Suggests potential issues with converters or inverters.
Common Causes of Electrical Failures
Several factors can contribute to electrical issues, including:
- Faulty wiring connections, which may create shorts or broken circuits.
- Blown fuses from overloading circuits.
- Bad converters or inverters that fail to supply the correct voltage.
Addressing Tripped Circuit Breakers
Tripped circuit breakers are common indicators of excess load; finding the caused appliance connected to that circuit can prevent future occurrences.
Key Takeaway:
- Recognizing symptoms early can guide prompt fixes.
- Familiarize yourself with the common causes of electrical failures.
- Address tripped circuit breakers immediately to prevent further issues.
Troubleshooting Electrical Components
When faced with electrical failures, a systematic approach to troubleshooting is essential. Start with identifying the specific problem and its possible root causes.
Testing Your Battery
The battery is the heart of your campervan’s electrical system. Monitoring voltage and ensuring connections are tight is critical:
- Check your voltage level; it should be between 12.3 – 12.9 volts. If lower, consider charging or replacing the battery.
- Inspect terminals for corrosion that may impede connection quality.
Checking the Converter and Inverter
To diagnose potential issues with these components, perform the following:
Regular Maintenance Tips
Regular checks can prevent unforeseen problems. Here are effective maintenance practices:
- Ensure all connections are tight and corrosion-free.
- Inspect the battery’s fluid levels for lead-acid types regularly.
- Perform voltage checks monthly to ensure reliability.
Key Takeaway:
- Regularly monitor battery voltage levels and maintain connections for optimal operation.
- Employ proper diagnostic methods to isolate issues with converters and inverters.
- Weekly or monthly maintenance can save time (and money) on repairs.
The Role of Converters and Inverters
Converters and inverters are integral for an efficient campervan electrical system, ensuring the proper power supply for various appliances.
Understanding What a Converter Does
Converters transform 120V AC shore power into 12V DC, allowing for battery charging and enabling low-voltage appliance operation. Failure to function can lead to dim lights and under-powered devices.
How Inverters Impact Power Supply
Inverters do the opposite, converting 12V DC battery power to 120V AC, catering to appliances like microwaves. A malfunctioning inverter may cause appliances to fail unexpectedly.
Common Inverter Problems
When inverters malfunction, common signs include:
- Lights flickering while using appliances.
- Power surges causing appliance shutdowns.
- Low battery voltage indicated by inverters failing to start.
Key Takeaway:
- Understand the critical functions of converters and inverters to avoid electrical errors.
- Be vigilant for signs indicating that your inverter or converter may be failing.
- Regular maintenance of these components can prevent devastating power failures.
Grounding Issues in Campervans
Proper grounding is crucial to ensuring safety and performance in campervan electrical systems. Grounding prevents electrical faults that could raise voltage levels dangerously.
Types of Grounding
Understanding grounding types is key:
- Chassis Ground: Connects the negative terminal from the leisure battery to the camper chassis, creating a common return path.
- Earth Ground: Involves grounding systems to the Earth for safety in high voltage situations.
Importance of Grounding
Effective grounding assures the following:
- Prevention of dangerous voltage levels during electrical faults.
- Protection for both your electrical system and yourself.
- Ensuring that appliances operate safely without risk of current leaking.
Troubleshooting Grounding Problems
When experiencing erratic behaviors in your electrical system, check the grounding connections:
- Ensure the grounding point is intact and secure.
- Inspect the connection for corrosion and integrity.
- Perform continuity tests to check for grounding faults in the system.
Key Takeaway:
- Proper grounding prevents serious safety hazards and operational issues.
- Identify type-specific grounding needs and maintain access for inspections.
- Regular checks of ground connections can save you from system failures.
Maintaining Battery Health
Batteries are vital to a campervan’s electrical system, serving as the primary power source. Understanding battery types and proper maintenance is essential for longevity.
Battery Types and Their Care
Common battery types include:
- Flooded Lead-Acid: Most common, requiring periodic water level checks.
- AGM (Absorbent Glass Mat): Less maintenance and more robust.
- Lithium: Higher performance but requires specific charge systems.
Charging and Maintenance Tips
Follow these tips for the best battery maintenance:
- Check voltage levels regularly (12.6—12.8 volts indicates a full charge).
- Use a battery maintainer when not in use.
- Clean terminals of any buildup that can hinder performance.
Signs Your Battery Needs Replacement
Be alert for signs indicating that your battery may be approaching the end of its lifespan:
- Repeatedly low voltage readings or failure to hold a charge.
- Corrosion buildup around battery terminals.
- Physical swelling or leakage.
Key Takeaway:
- Understanding battery types will help you provide appropriate care to prolong battery life.
- Regular voltage checks and maintenance will prevent sudden energy loss on the road.
- Recognizing signs of battery failure is crucial for timely replacement and avoiding inconveniences.
Importance of Regular Inspections
Regular safety inspections of your campervan’s electrical system can mitigate potential problems and save you time and money in the long run. Establishing a routine can enhance both safety and reliability.
Creating an Inspection Checklist
A comprehensive checklist is vital for maintaining the health of your electrical system. Here are some key inspection areas:
- Check battery health: voltage and terminal cleanliness.
- Inspect wiring connections for loose or corroded joints.
- Test fuses and circuit breakers for functionality.
- Review inverter and converter operation regularly.
Common Inspection Areas
Analysis of Table 2: This table outlines a systematic approach to inspections, helping campervan owners establish a practical framework for routine checks. It illustrates the importance of being proactive rather than reactive, providing insights into specific areas to monitor.
By implementing a structured inspection plan, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of facing unexpected electrical issues while on the road, allowing for smoother and more enjoyable travel experiences.
Benefits of Regular Maintenance
Regular inspections provide the following benefits:
- Early detection of potential faults or failures.
- Increased reliability of the electrical system.
- Reduced risk of unexpected malfunctions during trips.
Key Takeaway:
- A well-structured inspection plan can increase both safety and reliability.
- Frequent checks can help catch potential issues before they become significant problems.
- Maintain a record of inspections to track changes over time.
Troubleshooting FAQs
What should I do if my campervan batteries keep dying?
If your batteries are frequently dying, start by checking the battery voltage and charging system. Ensure connections are clean and tight and that you’re not overloading the system.
Perform regular checks on your converter and ensure it’s properly charging your batteries when connected to shore power.
If issues persist, consider consulting a professional.
How do I reset a tripped circuit breaker?
Resetting a tripped circuit breaker is simple. Locate your panel and find the breaker that is in the “off” position or is slightly ajar.
Firmly push it fully to the “off” position, then switch it back to the “on” position.
Check your attached appliances to ensure they’re not causing excessive load before resetting.
How can I tell if my converter is faulty?
When a converter is faulty, you might notice symptoms such as dimming lights when connected to shore power, failure to charge the batteries, or other appliances not functioning correctly. Performing a voltage test at the converter can determine its output; it should ideally be between 13.6 to 14.4 volts.
How often should I check my campervan’s electrical system?
It is advisable to conduct a thorough inspection of your campervan’s electrical system at least once every three months, with monthly checks on batteries and connections. Before embarking on long trips, ensure all components are fully functional.
What can I do to improve my battery’s lifespan?
To enhance your battery’s lifespan, routinely monitor voltage levels, avoid deep discharges, and maintain proper fluid levels (for flooded batteries). Using a battery maintainer during periods of inactivity and ensuring connections are corrosion-free will also contribute positively.
Conclusion
Navigating electrical issues in a campervan can seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and tools, many issues can be resolved. Ongoing maintenance, regular inspections, and an understanding of systems—from grounding to battery management—are essential for enjoying the campervan lifestyle.
Equipped with this guide, campervan owners can ensure a safe and functional electrical system, allowing for carefree exploration and adventures home on the road.