As the popularity of the RV lifestyle continues to surge, with many opting for extended road trips or working remotely from their RVs, the significance of a proper electrical setup cannot be overstated. While the idea of using an RV extension cord seems straightforward, it involves a labyrinth of important considerations crucial for safety and the longevity of appliances.
The right extension cord can make the difference between a blissful camping experience and catastrophic issues such as overheating or electrical fires.
According to data from experienced users, overloading cords and using low-quality materials are prevalent issues that can turn an idyllic getaway into a disaster. This comprehensive guide delves into common RV extension cord problems while providing actionable solutions to fortify the safety and effectiveness of your RV electrical system.
In this article, you will learn about essential aspects such as amperage ratings, wire gauges, and environmental impacts, empowering you to maintain an excellent RV experience.
Table of Contents
- Understanding RV Extension Cord Basics
- Common Safety Issues with RV Extension Cords
- Understanding Ampacity and Proper Usage
- Environmental Factors Affecting Extension Cord Performance
- Problems with Using Low-Quality or Cheap Cords
- Maintenance Tips for RV Extension Cords
- User Experiences and Reflections
- State Codes and Regulations for Extension Cords
Understanding RV Extension Cord Basics
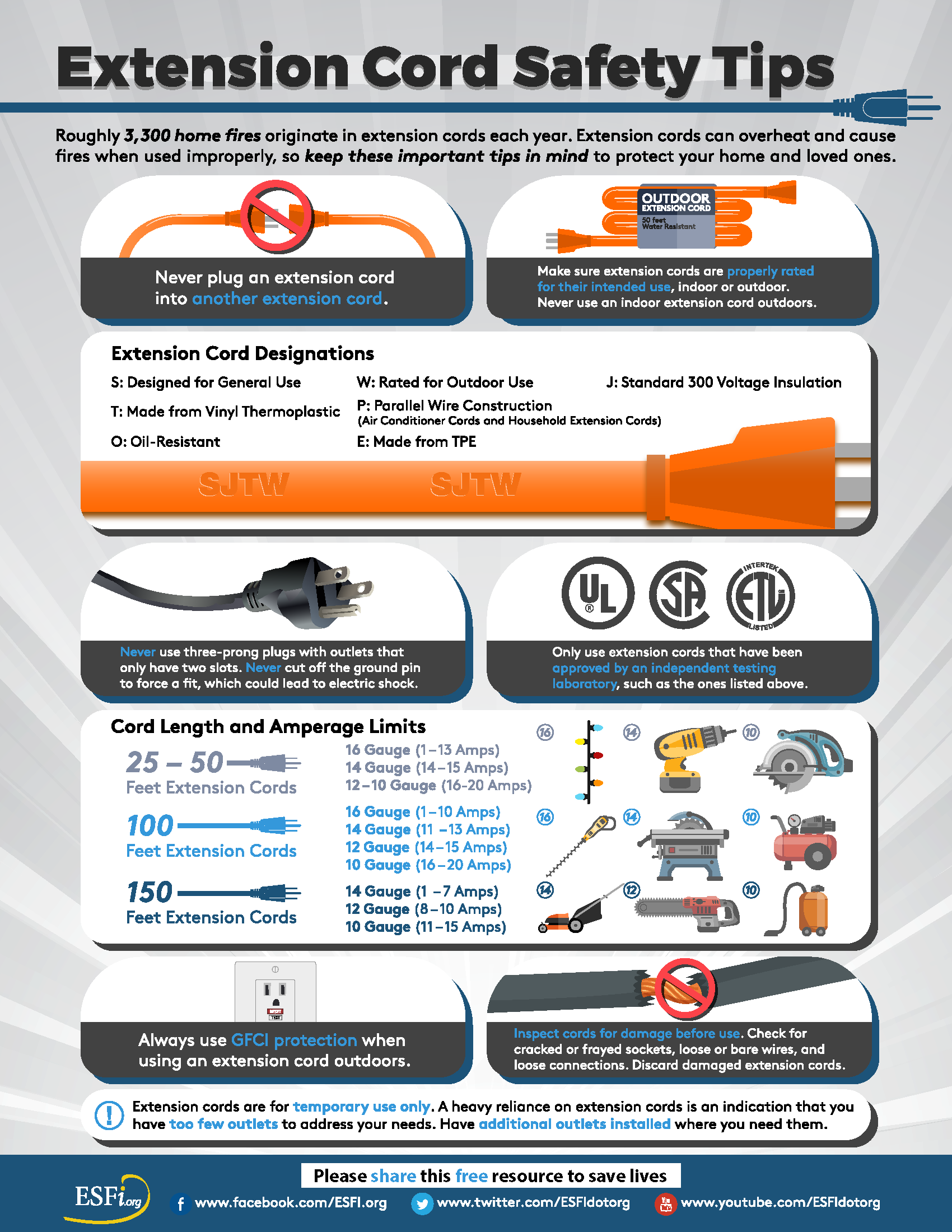
To safely utilize an RV extension cord, it’s paramount to grasp its purpose and construction. Designed specifically for handling high power loads, RV extension cords allow connection between RVs and outdoor power supplies or campsite outlets.
Understanding various gauges and ratings associated with these cords is the first step towards safe usage.
For example, a 20 Amp outlet necessitates an extension cord rated for at least 20 Amps. The wire gauge is integral to the cord’s capacity; while a 14-gauge wire is capped at 15 Amps, a 12-gauge wire can handle up to 20 Amps.
Selecting the correct gauge based on your appliance power consumption is crucial.
Outdoor application demands durability, meaning cords must withstand environmental wear and tear.
Wire Gauge and Amperage Rating
The wire gauge number is inversely related to the diameter of the wire; thus, a lower gauge means a thicker wire that can handle higher currents. For RV owners, understanding this relationship helps to prevent using inadequate extension cords that can lead to overheating.
When choosing a cord, you should account for the total amperes being drawn by the appliances in use.
For example, if your RV runs a heater (12 Amps) and a refrigerator (6 Amps), you are drawing a total of 18 Amps. In this case, using a 12-gauge wire would be advisable.
The above table clearly delineates the relationship between wire gauge and amperage ratings. It simultaneously provides insights into typical usage scenarios, helping RV owners choose the appropriate cord based on their needs.
For instance, while a 16 gauge cord suffices for minor appliances, it may pose risks when used for high-demand devices like air conditioners, which typically require 12 gauge for safe operation.
Usage for Temporary vs Permanent Applications
Using an RV extension cord for temporary setups, such as camping or short trips, is regular practice. However, many users also resort to extension cords for permanent applications, which, while convenient, raises safety concerns.
As discussed by RV enthusiasts, as long as the load remains within the cord’s rated capacity, temporary usage appears manageable.
However, prolonged exposure could lead to wear, overheating, and ultimately, failure of the cord or appliances. It’s vital to regularly inspect cords for signs of wear and to replace them if any signs of damage emerge.
- Comprehend wire gauge and amperage ratings to avoid overheating and other hazards.
- 12-gauge cords are ideal for high-powered appliances, while 14 and 16-gauge cords suit lighter appliances.
- Regular inspection is crucial for cords used in permanent applications to ensure safety.
Common Safety Issues with RV Extension Cords
The simplicity of using an RV extension cord can mask underlying safety hazards that demand attention. Some widespread safety issues arise from improper cord management, including overheating, cord damage, and faulty connections.
Overheating is a significant concern when appliances draw more power than the cord can handle, particularly with power-hungry equipment like air conditioners or heaters.
Moreover, users often overlook visible signs of cord damage, such as cracks or stiffness, which signal a potential fire hazard. Ensuring correct ratings and conducting regular inspections can mitigate many of these risks.
Overheating Risks
Overheating occurs when the electrical load surpasses the cord’s capacity, leading to a dangerous situation that could culminate in electrical fires. As mentioned in user experiences, running multiple high-consumption appliances simultaneously can easily trigger such overloads.
For instance, the combination of an air conditioning unit and multiple smaller devices could exceed safe amperage limits of common extension cords.
It’s essential to calculate total power usage and remain aware of what’s plugged in simultaneously.
This table illustrates how amperage adds up when multiple appliances are in use. A common scenario with a refrigerator and an AC unit could easily exceed 20 Amps, necessitating a higher-gauge cord to ensure safety.
Failure to comply with proper ratings increases the risk of overheating, thus, it’s critical to assess and limit usage effectively.
Inspecting for Wear and Tear
Regular inspections for wear and tear can prevent numerous hazards associated with RV extension cords. Users should routinely check cords for any visible damage, signs of brittleness, or cracking.
A simple rule of thumb is to replace cords showing such signs, even if they have not failed entirely.
Addressing corroded connectors and ensuring a clean, tight connection can significantly reduce electrical risks; users often overlook these details, leading to malfunctions.
- Overheating risks escalate with appliances drawing high amperage; ensure cords meet capacity.
- Conduct regular inspections for wear and tear to prolong safety and functionality.
- Corroded connectors can lead to faulty connections; clean and maintain regularly.
Understanding Ampacity and Proper Usage
Ampacity defines the maximum electrical current a conductor can safely carry without overheating. In RV applications, understanding ampacity is crucial for selecting appropriate extension cords.
For instance, if an RV typically operates at 30 Amps, drawing too much from a 20 Amp circuit risks overheating and failure.
Data from RV users emphasize calculating total amperage needed for appliances operating simultaneously to remain within safe limits.
Calculating Total Amperage Needed
To prevent overload issues, calculate the cumulative amperage drawn by devices in the RV. Each appliance has a specified wattage, which can typically be found on the unit itself or in the manual.
To determine amperage, use the formula: Amperes = Watts / Voltage.
For example, if your RV air conditioner is rated at 1500 watts, operating at 120 volts, it draws approximately 12.5 Amps. If you run a water heater (20 Amps) at the same time, the total exceeds safe limits on most circuits.
Choosing the Right Cord for Power Demands
Choosing the correct extension cord is essential for RV operations. Users may prefer higher gauge cords, particularly when running heavy appliances.
An excellent practice is to select cords rated slightly above the total amperage calculated.
Investing in a heavier gauge, such as 10-gauge for extended lengths, can help reduce voltage drop, ensuring the appliances receive adequate power without risking safety.
- Ampacity is vital in understanding safe summer power requirements for RVs.
- Calculate total amperage from all devices to avoid overloads.
- Opt for higher gauge cords for high-demand applications to ensure safety.
Environmental Factors Affecting Extension Cord Performance
Environmental factors can exhaust the integrity and safety of RV extension cords. The cords are often exposed to elements like UV light, moisture, and extreme temperatures, leading to degradation over time.
Though outdoor-rated cords help withstand some of these elements, regular inspections remain critical to maintaining performance and safety.
Impact of UV Exposure
UV light exposure can cause cord jackets to fade and degrade over time. When the protective outer layer deteriorates, the underlying wires become susceptible to damage, leading to potential safety hazards.
Users have experienced issues with corroded connections due to prolonged sun exposure.
As such, it’s essential to position cords away from direct sunlight when possible, extending their lifespan significantly.
Moisture and Temperature Considerations
Moisture exposure presents another risk, especially in humid areas. Condensation can cause wire insulation to break down, potentially leading to electrical shorts.
Moreover, temperature fluctuations can affect performance; extreme cold can make cords brittle while excessive heat can soften insulation, exposing wires.
Users often accommodate by storing cords in climate-controlled settings when not in use, which helps preserve their integrity.
The table above illustrates the impact of various environmental factors on extension cord longevity and performance. Notably, UV exposure can lead to significant degradation if cords are not adequately protected.
In addition, moisture poses a risk of corrosion, emphasizing the necessity of inspections, particularly in humid environments.
Lastly, protecting cords from temperature extremes can prevent both brittleness and softening—two factors that could compromise safety over time.
- Environmental factors like UV exposure and moisture can degrade extension cords.
- Regular inspections and preventive measures enhance cord longevity.
- Store cords thoughtfully to protect against temperature extremes.
Problems with Using Low-Quality or Cheap Cords
Many RV users may be tempted to opt for cheaper extension cords, but this decision can lead to critical failures and increased risks. Often, low-quality cords do not meet safety ratings and may be constructed from inferior materials, raising the likelihood of overheating and short-circuits.
Experiences shared by users reveal that saved money upfront can easily translate into costly repairs or replacement of burnt cords and appliances.
Identifying Cheap Cords
To avoid purchasing low-quality cords, look for reputable brands with appropriate safety ratings and certifications. Cheaper cords often skimp on factors like insulation quality, exposure resistance, and proper gauge ratings.
Users should be aware of telltale signs—cords that feel flimsy, lack proper labeling, or are made of suspicious materials typically indicate subpar quality.
Investing in trusted brands, while initially costlier, ensures durability and safety during RV operations.
Long-term Costs of Choosing Quality
While the upfront expense of quality extension cords is higher, the long-term cost savings are substantial. Users typically report that investing in adequate cords pays dividends in terms of reliability and avoidance of electrical failures.
As some RV enthusiasts noted, saved expenses over the long run on replacements and repairs often offset the initial investment for higher-quality cords.
The peace of mind from knowing your appliances are safe is worth the cost.
- Opting for low-quality cords can lead to significant safety risks and costly repairs.
- Identifying cheap cords by their quality and brand assurance is essential.
- Brands that emphasize quality and safety standards offer long-term savings.
Maintenance Tips for RV Extension Cords
Proper maintenance significantly enhances the lifespan and safety of RV extension cords. Owners are advised to check cords regularly for signs of damage, such as cracks or frays, and to replace them if degradation is noted.
Additionally, ensuring clean connections free from corrosion will keep your electrical setup optimal.
Users should also be aware of replacement guidelines; even if cords haven’t visibly failed, those showing wear may need replacement every few years.
Regular Inspection Practices
Conducting inspections is paramount. Owners should schedule routine checks for cords, focusing on connectors, insulation, and length.
Signs to spot include any visible cracking, brittleness, or discoloration.
Such early identifiers can prompt timely replacement before hazards emerge. Experts recommend using a checklist during these inspections to ensure all potential failure points are addressed.
Best Practices for Storing Cords
When not in use, storage techniques dramatically impact cord longevity. Cords should be stored without tight bends or kinks, which can compromise their integrity.
Winding them properly reduces physical damage while preventing tangling.
Ensure cords are coiled loosely, and store them in a dry, climate-controlled area when possible. Following these practices minimizes wear and prolongs lifespan.
- Regular inspections for wear and tear are essential to ensuring the longevity of cords.
- Store cords properly to prevent damage and ensure functionality.
- Be proactive in replacing worn cords even before visible failures occur.
User Experiences and Reflections
User experiences provide valuable insights into both the successful and problematic usage of RV extension cords. Many RV enthusiasts report using extension cords without incident, enjoying hassle-free electrical setups for years, whereas others encountered significant challenges leading to appliance failures or overheating issues.
As with any electrical system, following recommended guidelines for amperage and cord quality is crucial.
Learning from Success Stories
Users who adhered to outlined safety practices often regarded their experience as trouble-free. Many shared stories of long-lasting cords providing safe power for their appliances, including HVAC units and home office setups.
The correlation between good practices, such as regular inspections and quality cord selections, highlights effective management that extends beyond just choosing the right equipment.
Case Studies of Problems Faced
Conversely, accounts of failed appliances due to improper cord usage are invaluable lessons. One user recounted the time their air conditioning unit’s compressor failed two years in due to underpowering via a thin extension cord.
These cautionary tales serve to underscore the critical importance of respecting cord ratings and regularly assessing electrical needs to manage potential limitations effectively.
- Successful experiences highlight the importance of safety precautions in electrical management.
- Cautionary tales underscore the risk of misuse, making clear the need for responsible cord selection.
State Codes and Regulations for Extension Cords
Familiarity with local codes and regulations regarding extension cord usage is imperative for both legal and safety reasons. Many regions have strict guidelines governing the use of extension cords, particularly for RVs connected to electrical supplies.
From safety compliance to liability issues, failing to adhere to code can lead to dire consequences.
Key Regulations to Know
Common regulations may dictate proper usage, such as maximum allowable lengths for extension cords, permissible amperage ratings, and the required type of cord for outdoor use. Moreover, some jurisdictions specify the need for GFCI protection when cords extend outdoors or into humid areas.
Understanding and following these rules can protect against legal ramifications and keep users safe.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance with local electrical codes can bear significant repercussions. Users may find themselves facing fines, or worse, liabilities arising from accidents due to improper usage.
Moreover, many insurance policies stipulate compliance with local codes; failure to comply may jeopardize coverage in the event of an incident.
As such, staying informed on local regulations is a prudent course for all RV users.
- Understanding local extension cord regulations protects against legal issues and enhances safety.
- Be aware of codes concerning cord capacity and permitted usage to avoid fines.
- Compliance can also affect insurance coverage and liability mitigation.
FAQ Section
1. Can I use a regular extention cord for my RV?
Using a regular extension cord for an RV is not advisable. Standard extension cords typically lack the robust construction and amperage ratings necessary for high power loads associated with RV appliances.
It’s crucial to use RV-specific extension cords designed to handle the demands of your vehicles, thus mitigating risks of overheating and fire hazards.
2. How often should I replace my RV extension cord?
While there is no strict timeframe, it is recommended that RV extension cords be replaced every few years or upon the first signs of wear. Inspect cords regularly for any signs of brittleness, cracks, or other visible damage.
Early action can prevent safety hazards and ensure optimal operation of appliances.
3. What size extension cord do I need for my RV?
The size of the extension cord you need depends on the amperage draw of your RV appliances. Typically, a 12-gauge cord is necessary for running high-demand appliances like air conditioners, while 14-gauge may suffice for lighter duties.
Always check the amperage ratings required for your appliances and select an appropriate cord accordingly.
4. Are there specific regulations for using extension cords with RVs?
Yes, there are specific regulations that vary by jurisdiction. Many areas have guidelines regarding the maximum length of extension cords, required amperage ratings for outdoor use, and safety measures like GFCI protection.
Being aware of these regulations is critical for compliant and safe operation.
5. How can I tell if my extension cord is too hot?
Generally, an extension cord should feel warm—but not hot—when in use. If it becomes excessively hot to the touch, this could signify overuse or an underlying issue.
Look for symptoms like discoloration, visible damage, or a burning smell, and replace the cord immediately to avoid potential hazards.
Conclusion
Utilizing an RV extension cord entails careful consideration to avoid hazards and maintain functionality. The best practices highlighted throughout this article aim to equip RV owners with the essential knowledge needed to make informed decisions regarding their electrical setups.
Regular inspections, selecting the appropriate cords based on amperage ratings, and following safety guidelines all contribute to a safer, more enjoyable RV experience.
By approaching extension cord usage thoughtfully and responsibly, RV enthusiasts can focus on the joy of adventure instead of worrying about electrical failures.